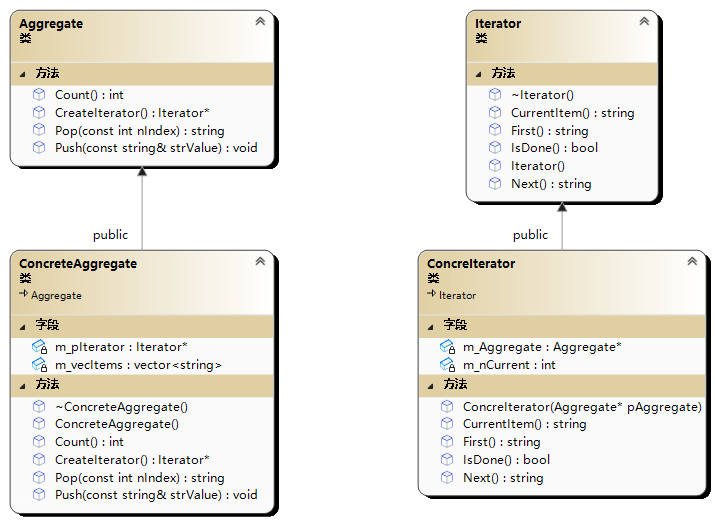
迭代器模式是一种行为型设计模式,它提供了一种顺序访问集合对象元素的方法,而无需暴露其底层实现。通过使用迭代器模式,我们可以在不了解集合内部结构的情况下遍历集合中的元素。
迭代器模式的核心概念是迭代器(Iterator)接口,该接口定义了访问和遍历集合元素的方法。具体的集合类实现迭代器接口,并提供了用于创建迭代器对象的方法。
使用迭代器模式的好处是,它将集合类的遍历行为与集合类本身分离开来,使得我们可以独立地改变遍历算法,而不需要修改集合类的代码。这样一来,我们可以根据不同的需求选择不同的遍历方式,而无需修改现有代码。
迭代器模式在实际应用中非常常见,例如在编程语言中的循环结构、容器类的遍历等场景都可以使用迭代器模式来实现。

#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//迭代器抽象类
class Iterator
{
public:
Iterator() {};
virtual ~Iterator(){}
virtual string First() = 0;
virtual string Next() = 0;
virtual string CurrentItem() = 0;
virtual bool IsDone() = 0;
};
//聚集抽象类
class Aggregate
{
public:
virtual int Count() = 0;
virtual void Push(const string& strValue) = 0;
virtual string Pop(const int nIndex) = 0;
virtual Iterator* CreateIterator() = 0;
};
//具体迭代器
class ConcreIterator :public Iterator
{
public:
ConcreIterator(Aggregate* pAggregate):Iterator(),m_nCurrent(0)
{
m_Aggregate = pAggregate;
}
string First()
{
return m_Aggregate->Pop(0);
}
string Next() {
string strRet;
m_nCurrent++;
if (m_nCurrent < m_Aggregate->Count())
{
strRet = m_Aggregate->Pop(m_nCurrent);
}
return strRet;
}
string CurrentItem()
{
return m_Aggregate->Pop(m_nCurrent);
}
bool IsDone()
{
return (m_nCurrent >= m_Aggregate->Count());
}
private:
Aggregate* m_Aggregate;
int m_nCurrent;
};
//具体聚集类
class ConcreteAggregate :public Aggregate
{
public:
ConcreteAggregate() :Aggregate(),m_pIterator(nullptr), m_vecItems({})
{
}
~ConcreteAggregate()
{
if (m_pIterator)
{
delete m_pIterator;
m_pIterator = nullptr;
}
}
Iterator* CreateIterator()
{
if (nullptr == m_pIterator)
{
m_pIterator = new ConcreIterator(this);
}
return m_pIterator;
}
int Count()
{
return m_vecItems.size();
}
void Push(const string& strValue) {
m_vecItems.push_back(strValue);
}
string Pop(const int nIndex)
{
string strRet;
if (nIndex < Count())
{
strRet = m_vecItems[nIndex];
}
return strRet;
}
private:
vector<string> m_vecItems;
Iterator* m_pIterator;
};
int main()
{
ConcreteAggregate* pName = new ConcreteAggregate();
if (!pName)
{
return -1;
}
pName->Push("hello");
pName->Push("world");
pName->Push("wanlu");
Iterator* iter = pName->CreateIterator();
if (!iter) {
delete pName;
return -1;
}
string strItem = iter->First();
while (!iter->IsDone())
{
cout << iter->CurrentItem() << endl;
iter->Next();
}
delete pName;
return 0;
}
//hello
//world
//wanlu